| PROGRAM |
| CONTENTS |
| REGISTRATION |
| ACCOMODATION |
| SUPPORT & PARTNERSHIPS |
|
ORGANIZATION: |
 |
|
COORDINATION: |
.png) |
+INFO: bimssc_2019@isep.ipp.pt

CURRICULAR PLAN:
The curricular plan of the course comprises a total of 90 hours of contact divided by 9 class modules and other activities:
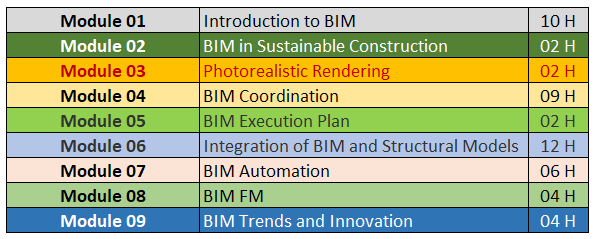
Along with the class schedule the Summer School program will include social events, visits to Portuguese AEC companies applying BIM methodologies and talks from invited speakers.
A supervised project will be developed and presented by all participants at the end of the course.
CURRICULAR PLAN PER MODULE:
|
01 |
Revit: Initiation Part I (2 h) & Part II (2 h): Navigating the Autodesk Revit workspace and interface. Standard terminology. Starting projects. Viewing commands. Creating levels and grids. Linking and Importing CAD Files. General modelling tools. Selecting, editing and modifying elements. Create section views and BOQs. Revit: Template definition and Management (2 h): Applying, modifying, creating and managing view templates. Creating and managing project templates. Using Family templates. Revit: Family Creation (2 h): Revit Families: System families, loadable families and in-place families. Creating family elements: Extrusions, blends, revolve, sweep and sweep blends. Adding tools: controls, Openings, lines, components. Creating Family Types. Visibility display settings. Understanding Instance and Type Parameters. Shared, family and project parameters. |
|
02 |
Integration of sustainable solutions from the first stages of design through BIM. Measuring holistic sustainability using BIM. |
|
03 |
Presentation of tools for the conversion of barebone 3d models to photorealistic renderings for images or animations including realistic backdrop context.
|
|
04 |
Revit: Federated Models (1 h): Linking Revit files. Positioning files according to coordinate system. Managing Links. Worksets. BIM Methodologies Coordination (1 h): BIM collaboration methodologies and technologies. Quality Control: visual checks, interference checks, standard checks and model integrity checks. BIM IFC (1 h): Overview on buildingSMART and openBIM. Introduction to IFC. IFC export from Revit. IFC viewer. Navisworks: Coordination (1 h): Navigating the Autodesk Navisworks workspace and interface. Standard terminology. Starting projects. Viewing commands. Linking files. Navisworks: Templates (2 h): The use of views on the creation of templates on Navisworks and their later application for additional exporting and application of consistent settings across views Navisworks: Clash Detection (2 h): Use of Navisworks for detection of interferences and collisions across multidisciplinary (Architectural, Structural and MEP) models, along with the extraction of comprehensive clash detection reports and help on conflict resolution. |
|
05 |
|
|
06 |
Robot Fundamentals II (2 h): Load definition and load combinations. Contours and panels. Finite element mesh generation. Calculation. Analysis of results based on diagrams and maps. Robot Steel Design (2 h): Steel design of metallic frames based on Eurocodes. Steel connection design. Drawings. Robot Reinforced Concrete Design (2 h): Methodologies of RC design: detailed and simplified. RC design of foundations, beams and columns based on Eurocodes. Drawings. Integration Robot-Revit Part I (2 h) & Part II (2 h): Structural tools, Analytical tools and parameters, Analytical model correction tools and Loads in Autodesk Revit. Model transfer to Autodesk Robot Structural Analysis (section and material mapping). Building analysis and design in Autodesk Robot Structural Analysis. Data transfer from Autodesk Robot Structural Analysis to Autodesk Revit (section and material mapping). |
|
07 |
Dynamo: Introduction (1 h): Navigating the Dynamo workspace and interface. Nodes, groups and organizing a script. Code blocks and lacing. Lis management. Custom Nodes and package manager. Dynamo: Creation of subroutines in Revit (2 h): Placing families through dynamo. Creating a wall along a line. Linking data between excel and a MEP model. Converting a CAD drawing into a Revit model. Dynamo: Creation of subroutines in Robot (2 h): Introduction to structural analysis for dynamo package. Creating a 2D Frame. Creating a 3D dome. Creating a 3D Frame. |
|
08 |
Design strategies for short, medium and long-term needs and optimization of real estate portfolios with metrics, automation, with BIM integration. |
|
09 |
|
.png)
Instituto Superior de Engenharia do Porto
Rua Dr. António Bernardino de Almeida, 431
4249-015 Porto
Portugal
| GPS: | 41°10'41.50"N |
| 8°36'24.37"W |



































